1. Immediate Health Risks of Smoking
A. Cardiovascular Problems
Smoking dramatically increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes, such as nicotine and tar, lead to the constriction of blood vessels and elevated blood pressure, which in turn heightens the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Nicotine causes blood vessels to narrow, raising blood pressure and exacerbating cardiovascular issues. Additionally, other toxic components in cigarette smoke contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, further increasing the risk of atherosclerosis.
B. Respiratory Issues
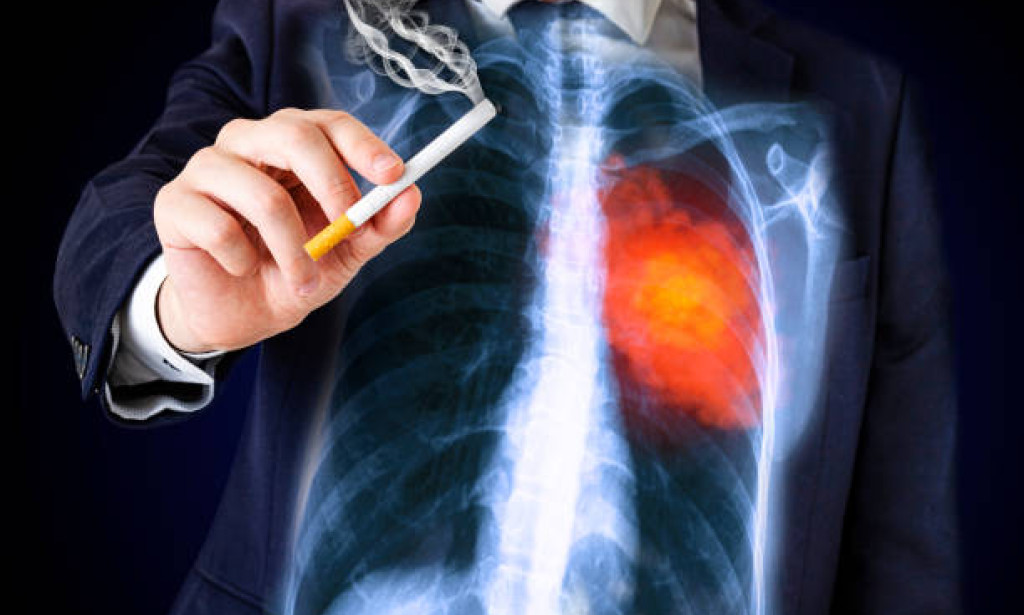
Smoking is a major contributor to respiratory problems. It leads to chronic bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and significantly increases the likelihood of developing lung cancer. Smoking impairs lung function, making breathing difficult and causing frequent coughing. The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke damage lung tissues and worsen respiratory conditions.
C. Other Types of Cancer
The detrimental effects of smoking extend beyond the lungs to other cancers, including those of the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, and pancreas. Cigarette smoke contains chemicals that cause cellular changes and mutations, leading to cancer development. The accumulation of these harmful substances accelerates cancer progression.
2. General Health Effects of Smoking
A. Weakened Immune System
Smoking compromises the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Smokers also experience slower recovery from diseases and injuries compared to non-smokers. The toxic chemicals in cigarette smoke weaken the body's ability to fight infections and viruses, reducing immune function.
B. Premature Aging
One of the visible effects of smoking is accelerated aging. Smoking damages the skin, leading to early wrinkles and negatively impacting overall skin appearance. The chemicals in cigarettes break down collagen and elastin in the skin, resulting in premature signs of aging.
C. Impact on Pregnancy and Children's Health
Smoking during pregnancy can cause various health problems for the fetus, including preterm birth, low birth weight, and an increased risk of congenital abnormalities. Children exposed to secondhand smoke are more likely to suffer from respiratory problems and other health issues. Secondhand smoke exposure poses significant risks to both mothers and their children.
3. Environmental Impact of Smoking
A. Air Pollution
Cigarette smoke contains many toxic substances that contribute to air pollution. This pollution affects air quality, which harms everyone's health, particularly vulnerable groups like children and the elderly. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke degrade air quality and affect both human and environmental health.
B. Waste
Smoking produces substantial environmental waste, such as cigarette butts, which take a long time to decompose. These butts contain toxic chemicals that can contaminate soil and water. Additionally, cigarette waste can result in long-term environmental damage.
4. Solutions and Future Directions
A. Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about the dangers of smoking through campaigns and educational programs can help reduce smoking rates. Educating the public about the health and social consequences of smoking is essential in encouraging individuals to quit. Awareness efforts should provide clear and accurate information about the impact of smoking.
B. Cessation Support
Providing support programs for quitting smoking, including medical counseling, nicotine replacement therapy, and psychological support, can be highly effective in helping individuals quit. These programs should be comprehensive and offer the necessary assistance throughout the quitting process.
C. Policy Measures
Enforcing strict policies, such as banning smoking in public areas, increasing taxes on cigarettes, and prohibiting tobacco advertising, can positively influence smoking rates. Government policies should be supported by effective enforcement and incentives to reduce smoking.
Conclusion
Smoking is not merely a harmful habit but a significant health risk that also negatively impacts the environment. Addressing this issue requires a collective effort from individuals, governments, and communities to reduce its harmful effects. By increasing awareness and providing adequate support, we can work towards a smoke-free future and lessen the burden of smoking-related diseases on society.
Continued efforts to combat smoking are crucial for improving public health and protecting the environment for future generations.

You must be logged in to post a comment.