Understanding Motherboards: The Heart of Your Computer
The motherboard is a critical component of any computer, serving as the backbone that connects all other hardware parts and allowing them to communicate with one another. Often referred to as the mainboard or system board, a motherboard houses the CPU (Central Processing Unit), RAM (Random Access Memory), and provides slots and interfaces for other components such as graphics cards, storage devices, and peripherals. In this article, we will explore the anatomy of motherboards, their types, features, and the roles they play in modern computing.
Anatomy of a Motherboard
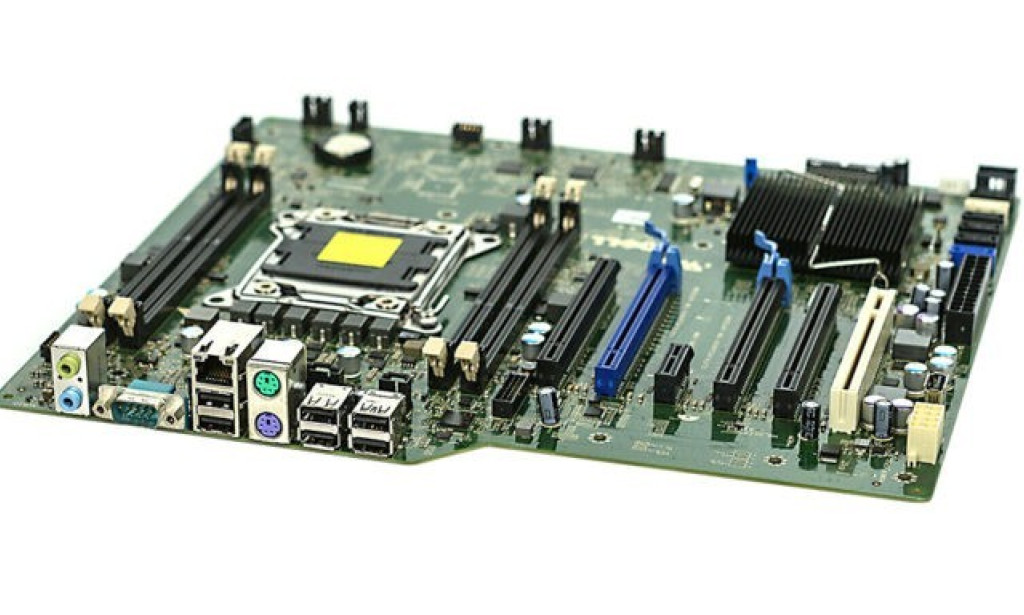
A typical motherboard consists of a large printed circuit board (PCB) with various integrated circuits, capacitors, and connectors. The main components of a motherboard include:
1. **CPU Socket**: This is where the processor is installed. Different CPUs require specific socket types; for example, Intel chips generally use LGA sockets, while AMD uses AM sockets.
2. **RAM Slots**: These slots are where the RAM sticks are inserted. Most motherboards support dual-channel or even quad-channel memory configurations, which enhance performance by allowing multiple memory modules to work in tandem.
3. **Chipset**: The chipset consists of two main parts: the Northbridge and Southbridge. The Northbridge manages communication between the CPU, RAM, and high-speed graphics slots, while the Southbridge handles slower, peripheral communications, including USB, SATA connections for storage devices, and expansion slots.
4. **Expansion Slots**: These are used to install additional components such as graphics cards (PCIe slots), sound cards, and network cards. The number and type of expansion slots vary by motherboard model.
5. **Storage Connectors**: Motherboards usually come with a combination of SATA ports for traditional hard drives and SSDs, and M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs, which provide much faster data transfer speeds.
6. **I/O Ports**: Located on the rear panel of the motherboard, I/O ports include HDMI, DisplayPort, USB, Ethernet, and audio jacks. These ports facilitate connectivity with external devices such as monitors, speakers, and network cables.
7. **Power Connectors**: To power the motherboard and connected components, power connectors are essential. The 24-pin ATX power connector is common for supplying power to the motherboard, while an additional 4 or 8-pin connector is used for the CPU.
Types of Motherboards
Motherboards come in various form factors, which dictate their size and layout. The most common types include:
1. **ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended)**: The standard for most desktop computers, ATX motherboards measure 305mm x 244mm. They provide multiple expansion slots and ample space for powerful components.
2. **Micro-ATX**: Slightly smaller than ATX, Micro-ATX motherboards measure 244mm x 244mm. They maintain compatibility with ATX cases but offer fewer expansion slots, making them ideal for budget-conscious builds.
3. **Mini-ITX**: Compact and designed for small form factor builds, Mini-ITX motherboards measure 170mm x 170mm. Despite their size, they support high-performance components, making them popular for home theater PCs (HTPCs) and space-saving setups.
Key Features to Consider
When selecting a motherboard, several features are critical to ensure compatibility and performance:
- **Chipset Compatibility**: Check the motherboard’s chipset to confirm it supports the CPU generation and features you need. For instance, certain chipsets allow overclocking, while others do not.
- **Memory Support**: Verify the maximum RAM capacity and speed supported by the motherboard. Different boards offer varying support for DDR4 or DDR5 memory.
- **Expansion Options**: Consider your needs for future upgrades. Look for motherboards that provide enough expansion slots and ports for additional components.
- **Cooling Solutions**: Many motherboards come with built-in cooling features or support for aftermarket solutions. Effective cooling is essential for maintaining performance, especially in high-load scenarios.
The Role of Motherboards in Modern Computing
Motherboards continue to evolve with advancements in technology. They are becoming more integrated, offering features such as built-in Wi-Fi, Bluetooth capabilities, and enhanced audio solutions. With the rise of gaming, high-performance motherboards tailored for gaming PCs offer RGB lighting, high-quality capacitors, and improved power delivery to ensure stability during demanding tasks.
In conclusion, the motherboard plays an indispensable role in computer functionality. Understanding its components, types, and key features can help users select the right motherboard for their needs, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility. Whether you're building a custom PC or upgrading an existing one, investing time in choosing the right motherboard will yield long-term benefits in productivity and enjoyment.

You must be logged in to post a comment.