 Electrolysis is the decomposition if compounds which takes place when electric current passes through a solution..
Electrolysis is the decomposition if compounds which takes place when electric current passes through a solution..
An in eletorlysis we have some few term inciend in it..
1. Eletorlyte : it is a compound either in solution or molten form which conduct electric current and decompose at the electrodes in the processe. Eg acid , and soluble salt .
2. Electrodes: these are poles either carbon or metal which electric current passes in or out of the eletorlyte.
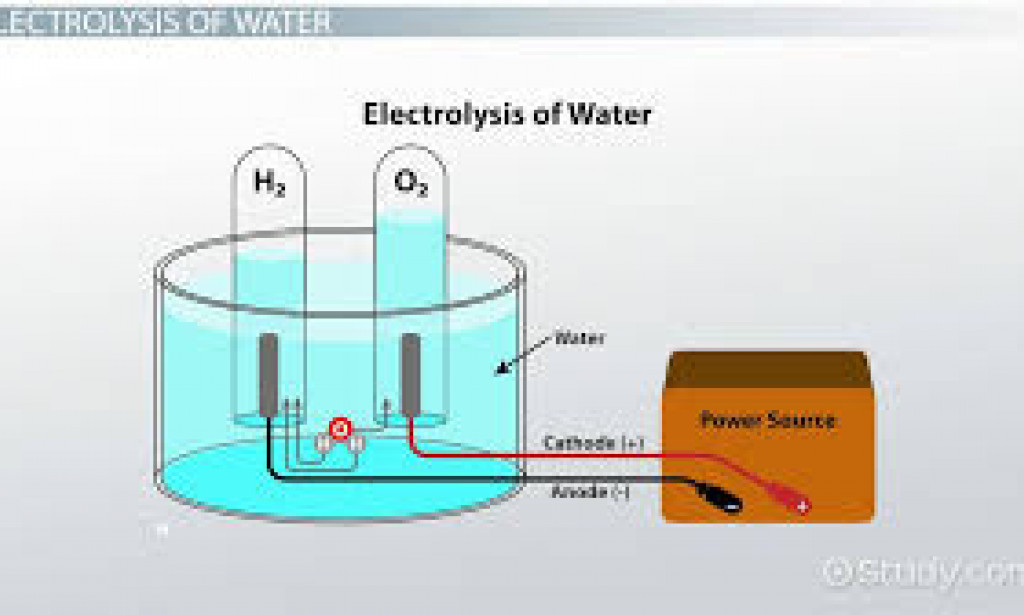
3. Anode : This are negative electrodes by which the charges or current enters the electrolyte.
4. Cathode : this are negative electrodes or poles by which the current enters the electrolyte.
5.Electrolytic cell: This consist of a container of electrolyte with two electrodes connected to a suitable direit current supply. In this cell oxidation occurs in anode an reduction at the cathode .
IONIC THEORY
This is when an electrolyte is melted or dissolved in water some , if not all the substance breaks up into freely moving charged particular called IONS.They process of dissociation or breaking into pieces of the ions is call IONIZATION Occurs before an electric current is passed into the electrolyte an the ions move about at random in all direction.
When electric current is passed through the eletorlyte, the free moving ions lose their random movement . Here some changes occure , where by the anode which are the positive ions are attracted to the cathode an are konw as cations. The negatives ions are then move to the anode an are called anions.
None metallic ion is formed form the atom , by gain of electron equals in number to the valency of the atom.
ELETORLYTE AND NON ELETORLYTE

An Eletorlyte conduct eletircity only when molten or in solution as a result of the movement of its ions to the electrodes.
Such more electrolytes carry in two classification.
1.Strong electrolytes
2.weak eletorlytes .
strong electrolytes : strong eletorlyte lonize completely in solution and conduct large current of electricity,and they are composed entirely of free moving ions.eg sodium chloride .other examples are soluble salt's and alkalis.
Weak Electrolytes:here ions ,ionize slightly an do not conduct eletircity.eg ammonia solution in water ,other examples includes ethanoic acid an citirc acid .
The non electrolytes do not conduct electricity but the are convalent in nature eg sugar .
Metallic conductor carry electric current both in soild an liquid state by atom move form one atom to an other.
But in Electrolytes it conduct when in molten or solution as a result of the movement of ions to electrodes.
DISCHARGE OF IONS DURING ELECTROLYSIS.
In this process two ions will be present in the solution . But the selection of ions discharge depends on
1.position of ion in electrochemical series
2. Concentration of the ions
3. Nature of the electrodes.
1. Position of ions in electrochemical series: here electrochemical series are discharge in preference to those higher up In the series. This is because the more electronegativity an ion will have the greatest tendency to accept electrons .
2. Concentration: an increase in concentration an ions tend to promote it's discharge from solution. However the concentration is effective only wheen the two competing ions are closely positioned in the electrochemical series an minimal when the ions are widely separated in position.
3. Nature vof electrode: electrons are discribe as when electrodes don't take part in Electrolytes reactions. Electron influence the ionic discharge because they posse carbon properties.
LAW'S OF ELECTROLYSIS
A scientist Michael faraday in a year 1833 after a series big electrolysis experience put forward two laws. I summary the laws state that the amount of substance liberated at the electordes during ELECTROLYSIS depends on.
1. Magnitude of the steady current passes.
2. Time of passing the steady current.
3.charge on the ion of the elements liberated.
The first law state that electrodes liberated during eletrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity (Q)passing through the electrolyte.
The second law states that when the same quantity vof electricity is passed through different Electrolytes, number of moles of elements deposited are inversely proportional to the charges on the ions of the elements.
USES OF ELECTROLYSIS.
1. Extartion of metal and non metal
2.purification off metals
3.Eletroplating of one metal of another's
4. Industrial preparation of certian chemical
You must be logged in to post a comment.