Definition of Hypertension
Hypertension, also commonly known as high blood pressure, is a medical condition in which the pressure (force ) of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high.It is the most leading cause of death ever recorded, and it
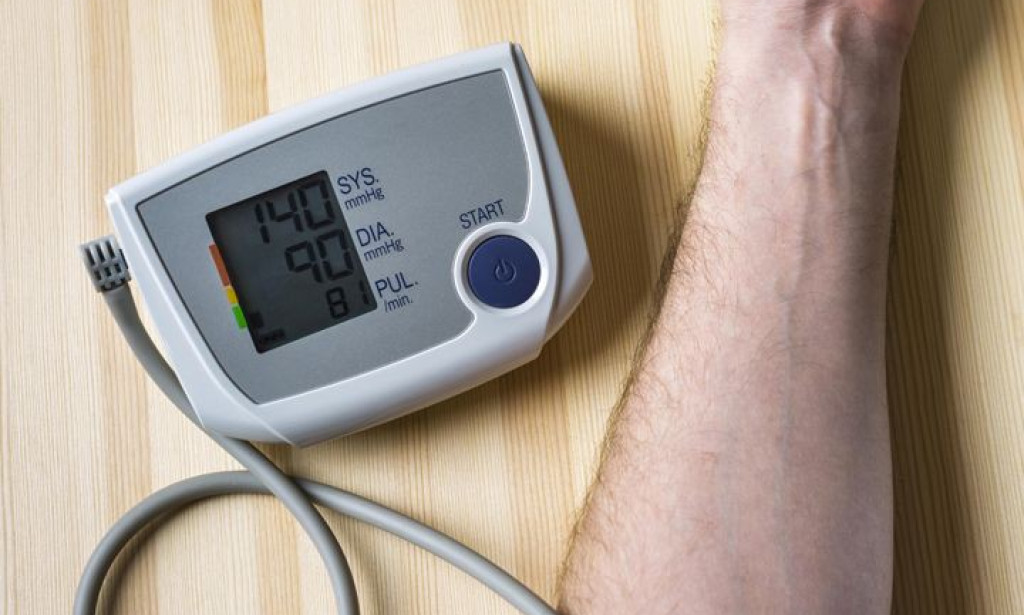
It is measured with a device called sphygmomanometer, though in a simple language, it's called Blood Pressure Reading Device, its value is determined using two numbers: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
A normal blood pressure reading is around 120/80 mmHg, while hypertension is diagnosed when the readings persistently exceed 130/80 mmHg.
Hypertension is often asymptomatic, so, it does not typically cause noticeable symptoms, some persons may experience early warning signs. If you notice any of these symptoms, it's crucial to consult your doctor for further diagnosis.
These are some of the early symptoms that may be associated with hypertension:
Sleepless Night: if you are having problem falling or staying asleep for as long as possible, it's definitely advised that you need to see a doctor to get your blood pressure checked,
Headaches: Frequent headaches, especially in the morning, can sometimes be an early indication of hypertension.
Fatigue or confusion: Feeling unusually tired or experiencing confusion and difficulty concentrating can sometimes be associated with hypertension.
Vision problems: Blurred vision or changes in vision clarity may occur in some individuals with high blood pressure. If you notice any sudden or persistent changes in your vision, it's essential to seek medical evaluation to determine the cause.
Chestpain: While chest pain is more commonly associated with heart-related conditions, it can occasionally be linked to hypertension. If you experience chest discomfort or pain, especially if it's accompanied by other symptoms like shortness of breath, it's advised for you to consult your doctor
5. Dizziness or lightheadedness: Feeling dizzy or lightheaded can sometimes be a symptom of high blood pressure.
Now you have known what Hypertension is, let's dive into the big Lies about it.
Lie No 1.
Hypertension only affects Older Individuals
It's a common misunderstanding, but let's set the record straight; hypertension can strike anyone, regardless of age. Although the likelihood of developing high blood pressure rises as we grow older, our lifestyle can push our blood pressure up at any stage of life.
Factors like an unhealthy diet, not getting enough exercise, and carrying excess weight can all play a role in raising our blood pressure, no matter how young or old we are. So, it's important to pay attention to our lifestyle habits and take steps to keep our blood pressure in check, regardless of our age.
Lie No 2.
Hypertension is primarily caused by stress
Although stress can cause a temporary spike in blood pressure, long-term hypertension is usually influenced by different factors. These include genetic predisposition, an unhealthy diet that's high in sodium and low in potassium, lack of physical activity, being overweight, and having certain medical conditions like kidney disease or hormonal disorders.
While managing stress is important for our overall well-being, it's equally essential to tackle these other risk factors to effectively control and manage hypertension.
Lie No 3.
Hypertension doesn't always come with noticeable symptoms.
Hypertension is referred to as the "silent killer". It often sneaks up on people without giving them any clear warning signs. That's why it's crucial to get your blood pressure checked regularly, even if you're feeling perfectly fine. By keeping tabs on your blood pressure, you can catch any potential issues early on and take the necessary steps to manage it effectively. Don't let this "silent killer" catch you off guard, stay proactive and keep an eye on your blood pressure.
Lie No 4.
Medication is the only solution for hypertension
Medications can certainly help in managing hypertension, but it's important to remember that making positive changes in your lifestyle can also make a big difference. By adopting a healthier diet that includes less sodium and more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, engaging in regular exercise, keeping your weight in check, limiting alcohol intake, and quitting the smoking habit, you can effectively lower your blood pressure.
Infact, these lifestyle adjustments will even allow you to decrease the amount of medication you take or, in some cases, stop taking it altogether with guidance from your doctor. Taking charge of your lifestyle can go a long way in keeping your blood pressure under control and promoting overall well-being.
Lie No 5.
Once diagnosed, hypertension cannot be controlled
Hypertension is a chronic condition, but with appropriate management, it can be controlled effectively. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, taking prescribed medications, and regularly monitoring blood pressure, individuals with hypertension can maintain their blood pressure within a healthy range and reduce the risk of complications.
It's important to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate information and guidance on managing hypertension. They can provide personalized advice based on an individual's specific health condition and risk factors.

You must be logged in to post a comment.