Tonsillitis: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Summary
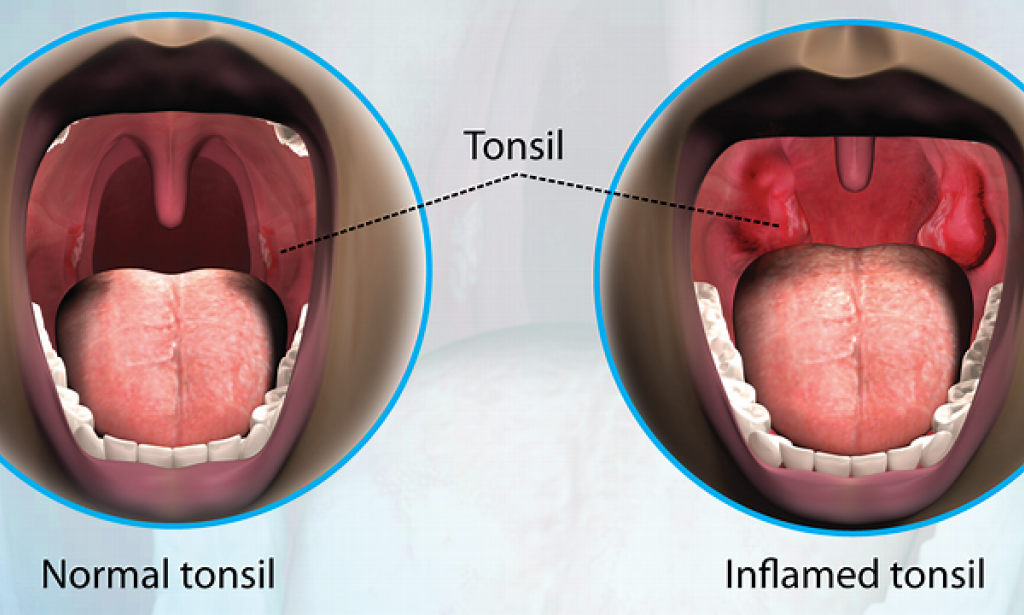
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils, which are soft tissue masses located at the back of the throat. This condition is usually caused by viral or bacterial infections and is contagious, spreading through coughing, sneezing, or direct contact.
Causes
Tonsillitis is primarily caused by viral or bacterial infections, with children being more susceptible. The infection spreads through:
- Respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing
- Direct contact with an infected person
- Contaminated objects, surfaces, utensils, and clothing
- Shared food or water
- Oral transmission
Symptoms
Common symptoms of tonsillitis include:
- Swollen, inflamed tonsils
- White or yellow patches on the tonsils
- Sore throat
- Difficulty or pain while swallowing (drooling in young children)
- Swollen and tender lymph nodes in the neck
- Stiff neck
- Fever
- Scratchy or muffled voice
- Bad breath
- Headache
Types of Tonsillitis
- Recurrent Tonsillitis: Short but frequent episodes occurring multiple times a year.
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Longer-lasting infections that persist for extended periods.
Diagnosis
Tonsillitis is diagnosed through physical examinations and laboratory tests, including:
- Physical Examination: Checking for throat infection signs, nasal and ear infections, and spleen enlargement.
- Lymph Node Examination: Gently palpating swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
- Throat Culture: Examining throat secretions under a microscope.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Assessing blood cell levels to determine the cause of infection.
Treatment
- Viral Tonsillitis: Managed with home remedies such as rest, hydration, and pain relievers.
- Bacterial Tonsillitis: Treated with antibiotics.
- Severe or Frequent Cases: May require tonsillectomy (surgical removal of tonsils).
Possible Complications
In children, bacterial tonsillitis (especially caused by Streptococcus bacteria) can lead to:
- Breathing difficulties due to throat obstruction
- Sleep disruptions due to breathing problems
- Spread of infection to deeper tissues (tonsillar cellulitis)
- Pus collection behind the tonsils
- Rheumatic fever, affecting the heart and joints
- Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, a kidney inflammation affecting waste removal
Prevention
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals
- Wash hands thoroughly before eating and after using the bathroom
- Do not share food, drinks, utensils, or personal items
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- Is the infection serious?
- Is surgery necessary?
- Should the patient be isolated?
- How can the infection be prevented?
- Do diet and lifestyle changes help in managing the condition?
Nutrition for Tonsillitis
Recommended Foods:
- Lukewarm beverages (e.g., clear juices, chicken broth)
- Soft foods (e.g., mashed potatoes, roasted carrots, plain pasta, rice)
Foods to Avoid:
- Hard, crunchy foods (e.g., pizza crusts, crackers)
- Hot or spicy foods

You must be logged in to post a comment.