Alpha-adducin gene
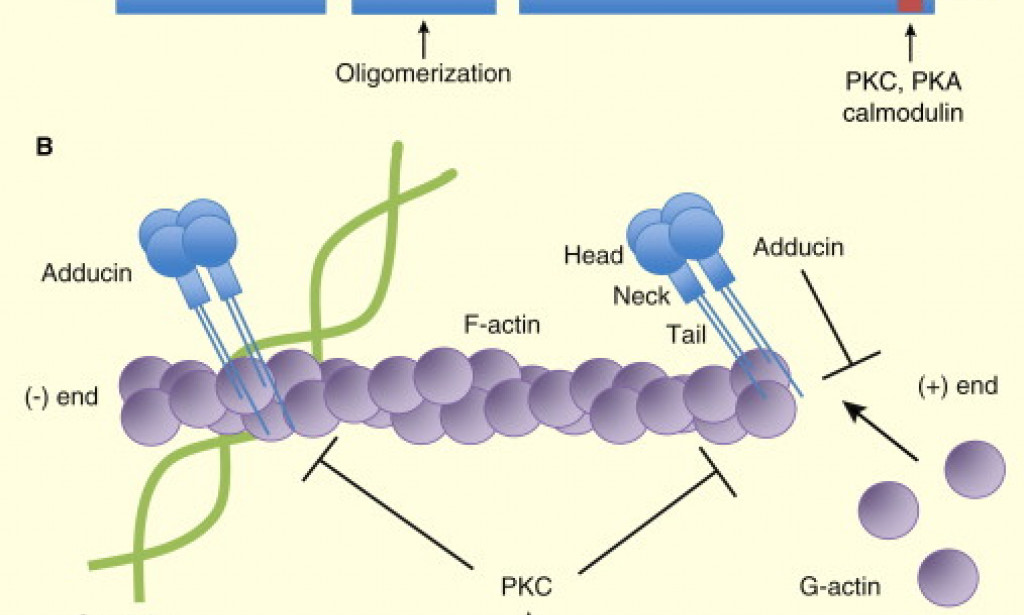
Adducin is membrane skeleton protein which consists of either A- and B- or A- and Y-subunits, which to a large extent are similar in amino acid sequence and domain organization. Adducin is also involved in the formation of actin-spectrin lattice by favoring the spectrin-actin binding and controlling the rate of actin polymerization as an end-capping actin protein (Joshi et al., 1991, Matsuoka and Li, 2000). In addition, protein kinases A and C, tyrosine, and ρ-kinases are involved in phosphorylation of adducin and also myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate protein family is involved in cell signal transduction (Matsuoka and Li, 2000).
Three human genes ADD1, ADD2, and ADD3 that map to different chromosomes encode A, B and Y subunits respectively ( Matsuka, et al., 2000 ). Besides, a gene encoding human alpha-adducin is located on chromosome 4p16.3 and contains 16 exons. In humans, two polymorphisms of the ADD1 gene lead to amino acid substitutions of Gly460Trp and S586C were identified (Cusiet al., 1997). There is a report that shows the abnormalities in adducin by genetic mutation influence influence the surface expression and maximum velocity of Na+K+/ATPase and subsequently faster renal tubular Na+ reabsorption (Mische, et al., 1987). There is also growing evidence that mutation of the alpha-adducin gene (ADD1) is associated with increased Na-K ATPase activity (Bianchi, et al., 2005) and increased renal tubular sodium reabsorption (Caulfielet al., 2003). Moreover, some studies have reported that the carriers of mutated ADD1 Trp allele have an increased risk of hypertension when compared with other homozygotes for the ADD1 G allele (Cusi, et al., 1997, Matsuoka, et al., 2003). A genetic variant in ADD1, namely, Gly460Trp polymorphism has been shown to be associated with renal sodium reabsorption, salt-sensitive hypertension and response to diuretic therapy (Glorioso, et al., 1999).
Alpha-adducin genes and Diuretics
Several studies have reported the association of ADD1 460Trp allele polymorphism with blood pressure, cardiovascular and stroke response to diuretics (Cusi, et al., 1997, Glorioso, et al., 1999, Psatyetal., 2002, Sciarrone, et al., 2003, Turner, et al., 2003). Details of these studies are presented in Table 5. Moreover, these studies have demonstrated that hypertensive individual with 460Trp should trigger less counter regulatory mechanisms, thus significantly reduced blood pressure and the risk of cardiovascular outcomes in response to diuretic treatment than the carriers of homozygous 460Gly allele in Italian subjects. For instance, a study done by Gloriosetal. (1999) on 143 hypertensive subjects who were treated for 2-month with hydrochlorothiazide, showed that blood pressure response to hydrochlorothiazide was better in patients carrying the 460Trp allele than the carriers of Gly460Gly allele. Similarly, the study that was conducted by Sciarrone, et al. (2003) with 87 hypertensive Italian subjects who were treated for 2-month with hydrochlorothiazide reported that the carriers of 460 Trp allele showed better blood pressure response to hydrochlorothiazide than those patients carrying Gly460Gly allele (Sciarroneet al., 2003). In addition, the study that was conducted by Manunta, et al. (2008) with 193 hypertensive Italian subjects who were treated for 1-month with hydrochlorothiazide reported similar results. According to that study, blood pressure response to hydrochlorothiazide was better in patients carrying the 460Trp allele than the carriers of Gly460Gly allele (Manunta, et al., 2008). Besides, population-based case-control studies on 1038 hypertensive patients who were treated for 10 years with different antihypertensive drugs identified that in carriers of the 460Trp ADD1 allele, the administration of diuretics halves the
Table 5: Summary of studies concerned to alpha-adducin gene Gly460Trp polymorphism and blood pressure response to diuretics, antihypertensive drugs.
|
Drug class & duration of therapy |
Genetics variants |
Ethnicity |
Sample size |
Significant differences |
Results (Bp response) |
References |
||||
|
Hydrochlorothiazide 2-months |
ADD1 Gly460Trp
|
Caucasians |
58 |
Yes |
460Trp carriers > Gly460Gly (MBP) |
Cusi et al., 1997 |
||||
|
Hydrochlorothiazide 2-months |
ADD1 Gly460Trp |
Caucasians |
143 |
Yes |
460Trp carriers > Gly460Gly (MBP) |
Gloriosoetal., 1999 |
||||
|
Hydrochlorothiazide, 4-years Observational studies |
ADD1 Gly460Trp |
Mixed |
1038 |
Yes |
460Wallele associated with a lower risk of CVD.
|
Psaty, et al., 2002 |
||||
|
Hydrochlorothiazide 2-months |
ADD1 Gly460Trp |
Caucasians |
87 |
Yes |
460Trp carriers > Gly460Gly (MBP) |
Sciarrone, etal., 2003 |
||||
|
Hydrochlorothiazide 4-weeks |
ADD1 Gly460Trp |
291 African Americans and 294 non-Hispanic whites |
585 |
No |
Gly460 = Trp460 (SBP and DBP) |
Turner,etal.,, 2003 |
||||
|
Chlorthalidone, amlodipinelisinopril, doxazosin 6-months |
ADD1 Gly460Trp |
- |
36913 |
No |
Gly460=Trp460 (SBP and DBP) |
Davis, et al., 2007 |
||||
|
Hydrochlorothiazide |
ADD1 Gly460Trp |
Dutch |
63 |
No |
Gly460 = Trp460 (SBP and DBP) |
Van WierendeWijer et al.,2009 |
||||
|
Drug class (subclass) |
Genetics variants |
Ethnicity |
Sample size |
Significant differences |
Results (Bp response) |
References |
|
|
b-blocker (Fluoxetine and paroxetine) |
ADD1 Gly460Trp |
USA White |
122 |
Yes |
|
Turner, et al., 2008b |
|
|
Hydrochlorothiazide 1-months |
ADD1 Gly460Trp |
- |
193 |
|
460Trp carriers > Gly460Gly, (SBP and DBP) |
Manunta, et al., 2008 |
|
|
Hydrochlorothiaz,amlodipine, bisoprolol, Losartan. 8-weeks |
ADD1 Gly460Trp 1166A/CMet235ThrSer49Gly,Gly389Arg |
Finnish men |
2006 |
No |
|
Suonsyrjä, et al., 2009 |
|
SBP= Systolic blood pressure DBP= Diastolic blood pressure
Bp= Blood pressure MAP= Mean arterial blood pressure
incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke when compared with other antihypertensive treatments that produce a similar reduction of BP. However, some of pharmacogenetics studies have failed to find significant association of ADD1 gene variants with diuretic mediated reduction in adverse cardiovascular events and stroke (Schwartz, & Eric Boerwinkle, 2003).In the most recent study including 613 hypertensive Dutch subjects didn’t report significant association of ADD1 Gly460Trp variants with BP response to hydrochlorothiazide treatments (van Wierende-Wijer, et al., 2009). Similarly, ADD1 Gly460Trp polymorphism has also not been found to influence BP response to HCTZ in Finnish subjects (Suonsyrjä, et al. 2009). Genetics of Hypertension-Associated Treatment Study (GenHAT) also did not find significant association of the Gly460Trp genotype with BP response to hydrochlorothiazide treatments, in a study with 36913 subjects (Davis, et al. 2007). In addition, a study including291 African Americans and 294 non-Hispanic whites subjects who were treated for 4-months with hydrochlorothiazide, couldn’t demonstrate significant association of Gly460Trp polymorphisms with BP response to hydrochlorothiazide (Turner, et al., 2003). A similar study on 5,979 hypertensive patients in USA showed a greater but non-significant association between Gly460Trp polymorphism and BP lowering effect of diuretics (Gerhard, et al., 2008).
In general, the selective beneficial effect of diuretics over the other drugs was not present in carriers of the Gly/Gly ADD1 genotype. Manunta, et al. 2007 reported in his review articles on adducing polymorphisms and hypertension that selective beneficial effect of diuretics over the other drugs in carriers of the 460Trp ADD1 allele support the notion that matching of the genetic mechanism with the drug mechanisms of action produces a clear benefit probably because the magnitude of the counter regulatory mechanism and, hence, the global cardiovascular risk may be minimized.


You must be logged in to post a comment.